What Are Some Tips for Optimizing Heating Temperature in Rotational Molding
 May 11,2025
May 11,2025

What Are Some Tips for Optimizing Heating Temperature in Rotational Molding?
The heating phase is a critical stage in the rotational molding process. During this phase, the temperature must be carefully regulated to ensure that the plastic powder melts uniformly and that the final product has the right physical properties, such as strength, durability, and dimensional accuracy. Improper heating temperatures can lead to a variety of issues, including incomplete melting, uneven wall thickness, warping, and surface defects. Below are some useful tips to optimize heating temperature for improving rotomolded products quality and production efficiency.
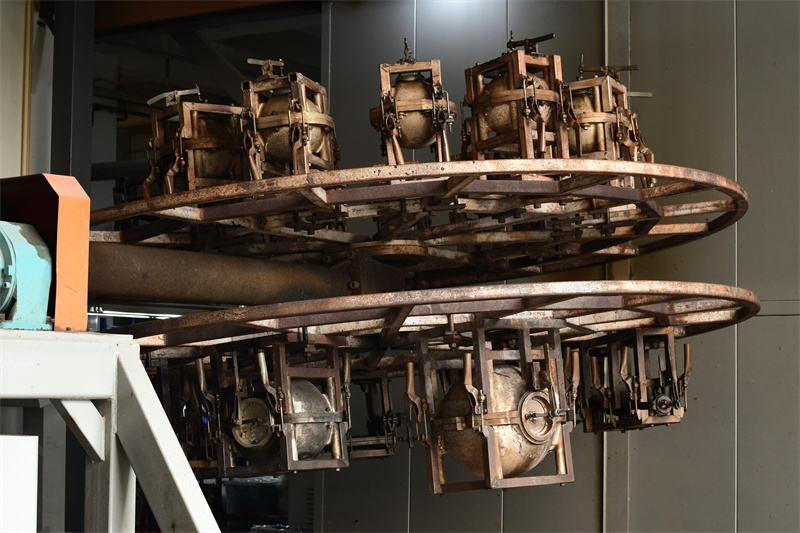

1. Select the Right Resin
The type of plastic resin used in rotational molding has a significant impact on the optimal heating temperature. Different resins have different melting points and heat sensitivity characteristics. For example, polyethylene (PE) is one of the most commonly used resins in rotational molding due to its excellent chemical resistance, impact strength, and low cost. PE typically has a melting range of around 120 - 135°C (248 - 275°F), but the specific melting point can vary depending on the grade and density of the PE resin. It is important to consult with a rotational molding supplier ensures the right temperature settings for your material.
2. Conduct Thorough Pre-Mold Preparation
Proper pre-mold preparation is essential for optimizing heating temperature in rotational molding. Before placing the mold in the oven, it should be thoroughly cleaned and preheated. Cleaning the mold removes any residual plastic, dirt, or debris that could affect the melting process and the quality of the final product. Preheating the mold helps to ensure that the plastic powder starts melting evenly as soon as it comes into contact with the mold walls.
The preheating temperature should be carefully controlled. It is usually set slightly below the melting point of the resin being used. For example, if using a PE resin with a melting point of 130°C, the preheating temperature might be set around 110 - 120°C. This gradual increase in temperature helps to prevent thermal shock to the mold and the plastic, reducing the risk of warping and other defects.
3. Monitor and Control the Oven Temperature
Accurate monitoring and control of the oven temperature are key to optimizing heating in rotational molding. Most modern rotational molding ovens are equipped with advanced temperature control systems that allow for precise setting and adjustment of the temperature. However, it's important to regularly calibrate these systems to ensure their accuracy.
During the heating process, it's recommended to use temperature sensors or pyrometers to monitor the temperature inside the oven and on the surface of the mold. This real-time data can help you identify any temperature variations or hotspots within the oven and make necessary adjustments to ensure uniform heating. For example, if one area of the oven is consistently hotter than others, you may need to adjust the airflow or reposition the mold to achieve more even heating.
4. Optimize the Heating Time
In addition to the temperature, the heating time also plays a crucial role in the rotational molding process. The optimal heating time depends on several factors, including the size and thickness of the product, the type of resin used, and the oven temperature. Generally, larger and thicker products require longer heating times to ensure that the plastic powder melts completely and evenly throughout the mold.
To determine the ideal heating time, it's often necessary to conduct test runs with sample molds and products. By analyzing the results of these test runs, you can fine-tune the heating time to achieve the best quality product. It's important to note that overheating can also be a problem, as it can cause the plastic to degrade, leading to reduced mechanical properties and surface imperfections. Therefore, finding the right balance between heating temperature and time is essential.
5. Consider the Cooling Process
The cooling process is an integral part of the rotational molding cycle, and it can also impact the effectiveness of the heating phase. After the plastic has been heated and melted in the mold, it needs to be cooled slowly and evenly to ensure proper solidification and dimensional stability. Rapid cooling can cause internal stresses in the plastic, leading to warping, cracking, or other defects.
To optimize the cooling process, it's recommended to use controlled cooling methods, such as forced air cooling or water cooling. The cooling rate should be carefully controlled to match the heating rate and the properties of the resin. For example, some resins may require a slower cooling rate to prevent thermal shock, while others can tolerate a faster cooling process. By coordinating the heating and cooling processes effectively, you can produce high-quality rotational molded products with consistent performance.
By following the tips outlined in this article, including selecting the right resin, conducting thorough pre-mold preparation, monitoring and controlling the oven temperature, optimizing the heating time, and considering the cooling process, manufacturers can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the rotational molding projects.
 Tel: 0086-13632687993
Tel: 0086-13632687993  Email: roto@lightvenus.com
Email: roto@lightvenus.com

 Home
Home What Are the Key Post-Demolding Inspection Points in Rotational Molding?
What Are the Key Post-Demolding Inspection Points in Rotational Molding?  You May Also Like
You May Also Like




 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address








